What is the Upper Explosion Limit (UEL)? Its Importance in Industrial Safety
In industrial safety, minimizing risks is not only about equipment quality but also about understanding the physical and chemical properties...
Devamını Oku
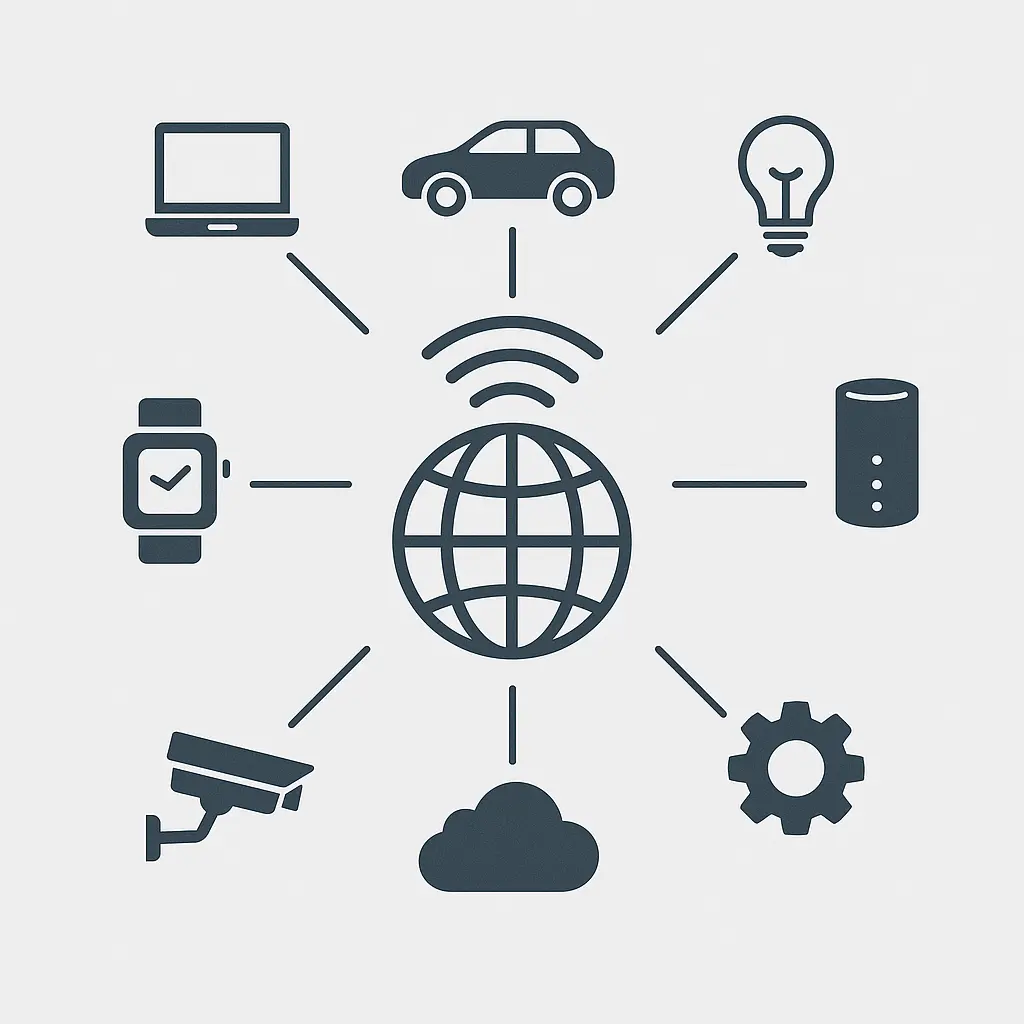
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity features to collect and exchange data. These devices range from household appliances and wearable technology to industrial machinery and smart city infrastructure. The core function of IoT is to enable seamless communication between devices and systems, without human intervention. This opens the door to real-time monitoring, automation, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making across numerous industries.
But what is IoT and what does it do in practical terms? It transforms passive objects into intelligent tools that can sense, analyze, and react to their environment. A smart thermostat can adjust itself based on your daily routine. A factory machine can alert technicians before a malfunction. IoT makes homes smarter, businesses more efficient, and cities more responsive. As technology advances, the IoT internet of things continues to reshape the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
IoT, short for the Internet of Things, is a technology ecosystem where physical devices are connected to the internet to collect, transmit, and act on data. These devices—ranging from smart refrigerators to factory sensors—can interact with each other and their surroundings. Unlike traditional devices, IoT-enabled objects are equipped with sensors, connectivity, and software that allow them to function autonomously. This helps streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and provide real-time insights across industries.
When asking what is IoT, it’s important to understand that it’s not limited to smart homes or gadgets. IoT is foundational to smart factories, healthcare systems, agriculture, energy management, and even city infrastructure. By allowing devices to communicate and act independently, IoT reduces downtime, enhances efficiency, and opens new opportunities for automation. Today, it’s at the heart of digital transformation and a critical tool in building smarter, more responsive environments.
The IoT acronym stands for “Internet of Things.” It describes the concept of connecting physical objects to the internet so they can send, receive, and process data. The “things” in this context can be anything from appliances and vehicles to industrial tools and sensors.
Understanding the iot expansion helps clarify its role in today’s digital landscape. It signifies a shift from isolated machines to interconnected ecosystems where data flows seamlessly, enabling automation, efficiency, and smarter decision-making.
IoT systems are the building blocks of the Internet of Things, consisting of connected devices, data transmission protocols, cloud platforms, and software applications. These components work together to collect environmental or operational data, transmit it securely, and analyze it to generate actionable insights. Whether it’s a wearable health monitor or an industrial sensor on a production line, every device plays a role in a broader system that enables automation and intelligence.
In practice, iot systems include sensors to gather data, network connections to send it, and software to interpret the information. These systems can trigger real-time actions, such as adjusting temperature in a smart home or alerting a technician before machinery fails. As they operate autonomously, they minimize human intervention while improving speed, accuracy, and resource efficiency. The scalability and flexibility of these systems make them ideal for various industries, from healthcare and logistics to manufacturing and energy.
Sensors are at the core of any IoT system, enabling devices to monitor temperature, humidity, motion, light, or pressure in real time. These sensors collect raw data from the environment, which is then transmitted to cloud platforms or local servers for processing. Accurate data collection ensures that the system responds appropriately to changing conditions.
This phase is essential because the value of an IoT solution depends heavily on the quality and timeliness of the data it gathers. Without reliable sensors, smart systems would be ineffective and inconsistent.
Software and connection networks are what bring IoT devices to life. Once sensors collect data, software platforms interpret, visualize, and act on that information. These platforms can automate actions, send alerts, or feed insights into other systems. Without software, IoT devices would just gather data without purpose.
The connection networks—such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or 5G—enable devices to communicate in real time. The reliability and speed of these networks directly impact system performance and are crucial for large-scale internet of things deployments across industries.
Inter-device communication allows IoT-enabled devices to share data and coordinate actions without human input. This machine-to-machine interaction ensures that systems operate more efficiently—for example, a motion sensor turning on lights or a thermostat adjusting temperature based on occupancy.
This communication is essential in complex environments like factories or smart homes, where devices must work together seamlessly to respond to real-time changes and optimize performance.
The Internet of Things spans countless industries and daily life scenarios, making it one of the most versatile technologies of the modern age. From homes to cities and agriculture to manufacturing, IoT is transforming how we interact with physical environments. In healthcare, wearable devices monitor patient vitals in real-time. In agriculture, smart irrigation systems use soil data to water crops more efficiently. Even retail businesses use IoT to track inventory and optimize supply chains.
Understanding the areas of IoT application helps answer the question, what is the internet of things in real-world terms. For consumers, it brings convenience and automation—think smart speakers, connected thermostats, or voice-controlled lighting. For industries, it delivers precision, efficiency, and predictive power. The technology’s ability to collect data and make instant decisions not only boosts productivity but also enhances sustainability and customer experience. IoT is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a practical solution for everyday challenges.
Smart home applications are among the most visible uses of IoT today. From voice-controlled assistants to automated lighting, security cameras, and smart thermostats, these systems enhance comfort, security, and energy efficiency. Devices communicate with each other to create personalized, responsive environments that adapt to the homeowner’s preferences and habits.
Smart homes illustrate how the iot transforms everyday life, bringing convenience and control through automation.
Industrial IoT systems (IIoT) are used in sectors like manufacturing, energy, logistics, and infrastructure to monitor operations, reduce downtime, and optimize performance. Sensors track machine health, environmental conditions, and energy use—providing data that helps businesses make smarter, faster decisions.
This form of iot internet of things integration brings automation to industrial environments, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time process control for safer, more efficient operations.
In smart cities, IoT is used to improve urban infrastructure, reduce congestion, and enhance public services. Traffic signals adjust based on real-time flow, parking sensors guide drivers to open spots, and environmental monitors track air quality.
These internet of things advantages create more sustainable and livable cities by optimizing resources and improving the daily lives of citizens.
The advantages of IoT are transforming the way individuals, businesses, and governments operate. At its core, IoT offers automation, efficiency, and real-time control—making systems smarter and more responsive. In homes, it enhances convenience and energy savings. In industries, it reduces downtime, boosts productivity, and enables predictive maintenance. Across the board, IoT minimizes manual intervention and accelerates decision-making through accurate, up-to-date data.
Another major benefit is improved resource management. Whether it’s optimizing water usage in agriculture or reducing energy waste in buildings, what is iot and what does it do often comes down to sustainability and cost-efficiency. It also plays a critical role in enhancing safety and security, as connected devices can monitor environments and trigger alerts during anomalies. As more devices become connected, the cumulative impact of IoT is reshaping daily life, business models, and even city infrastructures on a global scale.
IoT projects range from small-scale home automation setups to complex industrial ecosystems. These projects often involve custom hardware, cloud integration, and specialized software working together to solve real-world problems. For example, a smart farming project might use soil moisture sensors, weather data, and automated irrigation to improve crop yields. In logistics, IoT can track goods in transit, monitor temperature-sensitive shipments, and reduce delivery times.
Leading iot companies are driving innovation by offering end-to-end IoT solutions—spanning hardware development, software platforms, security frameworks, and data analytics tools. These firms support businesses across sectors like healthcare, transportation, energy, and retail. By collaborating with experienced providers, organizations can implement reliable and scalable IoT infrastructure tailored to their goals. As demand continues to grow, the question what are iot projects becomes more relevant for industries seeking competitive advantages in a connected world.

In industrial safety, minimizing risks is not only about equipment quality but also about understanding the physical and chemical properties...
Devamını Oku
Smart energy management refers to the use of advanced technologies and integrated systems to monitor, control, and optimize energy consumption...
Devamını Oku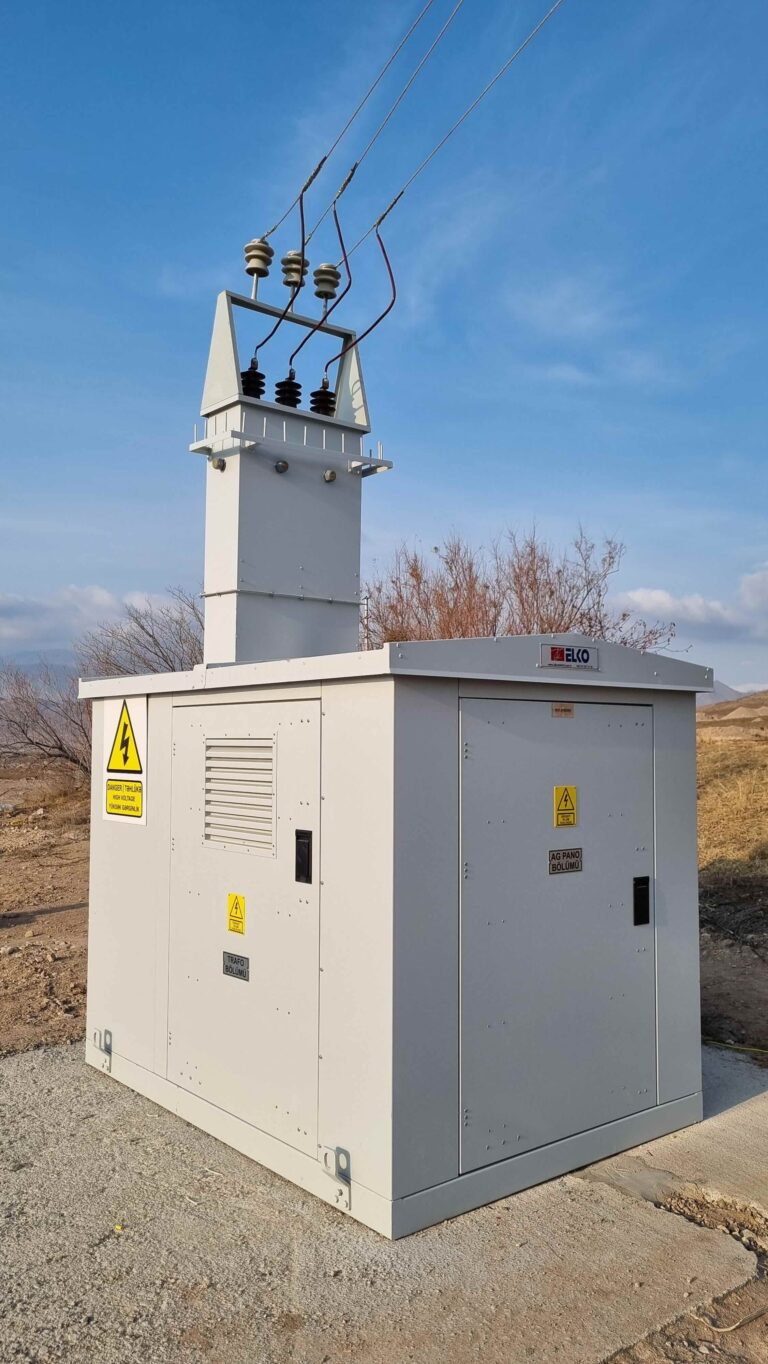
A transformer substation is a critical facility designed to convert electrical energy from high voltage to low voltage, ensuring safe...
Devamını OkuPROTECTION OF PERSONAL DATA
WEBSITE COOKIE POLICY
Your personal data; It is one of the leading principles of our Organization to protect the privacy of visitors to the website (www.adatech.com.tr) operated by ADATECH as the data controller. This Cookie Usage Policy (“Policy”) explains to all our website visitors and users which types of cookies are used and under what conditions.
Cookies are small text files stored on your device or network server by websites you visit on your computer or mobile device.
They are generally used to provide you with a personalized experience during your use of the website you visit, to improve the services offered and to improve your experience, and may contribute to ease of use while browsing a website. If you do not prefer the use of Cookies, you can delete or block Cookies in your browser settings. However, we would like to remind you that this may affect your use of our website. Unless you change your cookie settings in your browser, we will assume that you accept the use of cookies on this website.
1. WHAT KIND OF DATA IS PROCESSED IN COOKIES?
Cookies on websites, depending on their type, collect data about your browsing and usage preferences on the device you visit the site. This data includes information about the pages you access, the services and products you review, your preferred language option and other preferences.
2. WHAT is a solution and what are its intended uses?
Cookies are small text files that are stored on your device or network server through browsers by websites you visit. These small text files, which contain your preferred language and other settings on the site, help us remember your preferences the next time you visit the site and make improvements to our services to improve your experience on the site. Thus, you can have a better and personalized usage experience on your next visit.
The main purposes of using cookies on our Website are listed below:
3.TYPES OF COOKIES USED ON OUR WEBSITE
3.1. Oturum Çerezleri
Session cookies ensure that the website functions properly during your visit. They are used for purposes such as ensuring the security and continuity of our sites and you during your visit. Session cookies are temporary cookies, they are deleted when you close your browser and come to our site again, they are not permanent.
3.2. Persistent Cookies
These types of cookies are used to remember your preferences and are stored on your device via browsers. Persistent cookies remain stored even after you close your browser or restart your computer from which you visited our site. These cookies are kept in subfolders of your browser until they are deleted through your browser’s settings.
Some types of persistent cookies may be used to provide you with special suggestions, taking into account issues such as your purpose of using the Website.
Thanks to persistent cookies, if you visit our Website again with the same device, it is checked whether there is a cookie created by our Website on your device and if there is, it is understood that you have visited the site before and the content to be transmitted to you is determined accordingly and thus a better service is provided to you.
3.3. Mandatory/Technical Cookies
These cookies are essential for the website you visit to function properly. The purpose of such cookies is to provide necessary services by enabling the website to function. For example, it allows you to access secure parts of the website, to use its features, to navigate on it.
3.4. Analytical Cookies
They collect information about the way the website is used, the frequency and number of visits, and show how visitors navigate to the site. The purpose of using such cookies is to increase performance by improving the way the site functions and to determine the general trend direction. They do not contain data that could enable the identification of visitors. For example, they show the number of error messages displayed or the most visited pages.
3.5. Functional/Functional Cookies
It saves the choices made by the visitor within the site and remembers them on the next visit. The purpose of such cookies is to provide ease of use to visitors. For example, it prevents the site user from re-entering the user password on each page they visit.
3.6. Targeting/Advertising Cookies
They enable the measurement of the effectiveness of advertisements served to visitors and the calculation of the number of times the advertisements are viewed. The purpose of such cookies is to serve ads customized to the interests of visitors.
Likewise, they enable the detection of visitors’ interests specific to their browsing and the presentation of appropriate content. For example, it prevents the advertisement shown to the visitor from being shown again in a short time.
4. HOW TO MANAGE COOKIE PREFERENCES?
To change your preferences regarding the use of cookies or to block or delete cookies, simply change your browser settings.
Many browsers give you the option to accept or reject cookies, accept only certain types of cookies, or be alerted by the browser when a website requests to store cookies on your device so that you can control cookies.
It is also possible to delete cookies previously saved in your browser.
If you disable or refuse cookies, you may need to set some preferences manually, some features and services on the website may not function properly as we will not be able to recognize and associate your account. You can change the settings of your browser by clicking on the relevant link from the table below.
5. ENFORCEMENT OF WEBSITE PRIVACY POLICY
Website Privacy Policy …./…./…./…. . is dated. In case all or certain articles of the Policy are renewed, the effective date of the Policy will be updated. The Privacy Policy is published on the website of the Authority (www.adatech.com.tr) and made available to the relevant persons upon the request of the personal data owners.
ADATECH
Address: Esenyalı Neighborhood Yanyol Street Varyap Plaza No:61-148 Pendik / Istanbul
Telephone: +90 (216 ) 514 80 69
E-mail: [email protected]
Web Address: www.adatech.com.tr